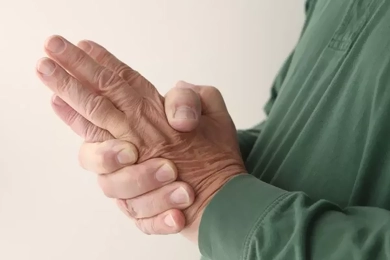
Have you ever thought about why we age? While aging is a natural process, recent research has shown a surprise component that accelerates it: chronic inflammation.
Consider inflammation to be your body's fire warning system. When you are injured or sick, your body responds by indicating that it needs to recover and defend itself. But what if the alarm continues to sound? This is where "inflamm-aging" enters the picture.
The Aging and Inflammation Vicious Cycle: Our bodies change as we age, and one key alteration is a persistent, low-level inflammation.
When Our Cells Tire: Our cells grow tired and strained over time. These worn-out cells produce substances that contribute to inflammation. This is analogous to a neighborhood party that becomes too loud and never stops, producing additional stress in the area (our body).
Our Immune System's Struggle: As we become older, our immune system, the body's defense force, becomes less efficient. It's analogous to an elderly police force struggling to keep up with the demands of the job, leaving us more susceptible to viruses and diseases.
Bone Marrow and Blood Cells: Our bone marrow, which generates blood cells, becomes less efficient, resulting in weakened immune cells. It's as if the factory that makes our bodies' warriors slows down and begins generating fewer effective ones.
Decline in Immune Cell Function: Immune cells such as neutrophils, macrophages, and T cells become less effective. Consider how your body's soldiers are getting older and slower, making it more difficult for them to guard you from infections.
Lymphoid Organs Wearing Out: Immune-producing organs such as the thymus and spleen wear out. This is analogous to your body's soldiers' training fields and barracks becoming less functioning.
Preventing or delaying the progression of inflammation requires a combination of lifestyle decisions, dietary changes, and maybe medicinal therapies. Here are some important strategies:
Mindfulness & Meditation: Mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing techniques have been shown to alleviate stress, which is a recognized contributor to inflammation.
Adequate Sleep: Getting 7-9 hours of excellent sleep each night aids in stress hormone regulation and inflammation reduction.
Hobbies and Social Connections: Participating in activities that you love and maintaining social contacts might help you feel better and minimize stress.
Monitor Health Parameters: Regular check-ups can aid in the early detection and management of illnesses associated with inflammation, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and obesity.
Consult Healthcare Providers: Always seek tailored advice from healthcare specialists, especially if you have underlying health issues.
Inflamm-aging is a complex process, but it can be considerably reduced by taking a holistic strategy that includes a balanced diet, frequent physical activity, stress management, and avoiding identified triggers. Before making significant changes to your diet or lifestyle, always discuss with your healthcare professional, especially if you have pre-existing health concerns.
In a Nutshell
Inflamm-aging is like a silent alarm that continues to sound even when there is no fire, causing our bodies to be on high alert. This condition hastens aging and increases the risk of age-related disorders. We may help our bodies age more gracefully and healthily by understanding this process and adopting proactive efforts. Remember that taking care of your body today is an investment in your future health!
 Factors Exacerbating Lipedema: Triggering Drugs, Foods, and Supplements
Factors Exacerbating Lipedema: Triggering Drugs, Foods, and SupplementsLipedema is a common chronic condition, particularly among women, that leads to abnormal fat accumulation in areas such as the legs and hips, significantly reducing the quality of life. This article discusse ...
 Understanding the Distinctions Between Lipedema and Lymphedema
Understanding the Distinctions Between Lipedema and LymphedemaLipedema and lymphedema are often confused due to their similar names and some overlapping symptoms. However, they are distinct medical conditions with different causes, treatments, and management strategies ...
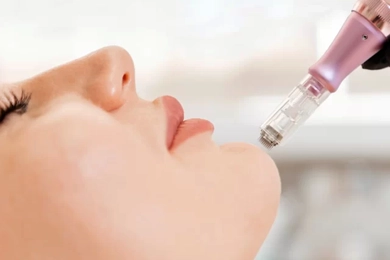 What is the Best Source of Exosomes?
What is the Best Source of Exosomes?Exosome therapy has emerged as an innovative treatment method for skin rejuvenation, hair loss prevention, wound healing, and immune support. The effectiveness of exosomes depends heavily on their source, ex ...
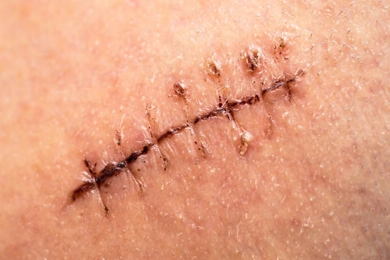 What Can Be Done to Prevent Stitch Scars?
What Can Be Done to Prevent Stitch Scars?Stitches, used after surgeries or injuries, help the skin heal but can often leave unwanted scars behind. The permanence of stitch scars depends on many factors, but with the right precautions, these scars c ...
 How to Get Rid of Surgical Stitch Scars?
How to Get Rid of Surgical Stitch Scars?After surgery, scars from stitches are often part of the healing process. These scars can cause aesthetic concerns for many, but with the right treatments, their appearance can be significantly reduced. So, ...
 How Does Stem Cell Therapy Reduce Surgical Scars?
How Does Stem Cell Therapy Reduce Surgical Scars?Surgeries are often vital steps to improve health, but they can leave behind scars that are particularly bothersome for those with aesthetic concerns. Traditional treatments may not always be effective enoug ...
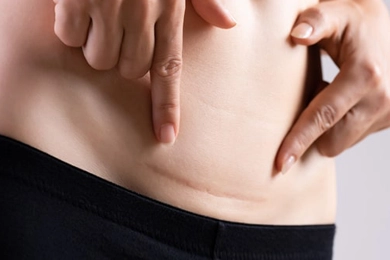 Does Stem Cell Therapy (SVF) Prevent Scar Formation on the Skin?
Does Stem Cell Therapy (SVF) Prevent Scar Formation on the Skin?Scarring is a natural part of the body’s healing process after injuries, surgeries, or trauma. However, excessive scarring can sometimes lead to aesthetic concerns or functional limitations. Recent studies s ...
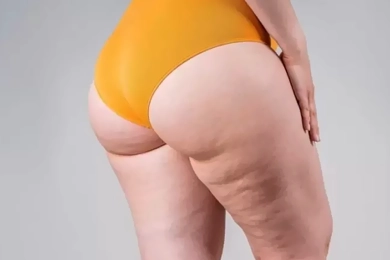 Advantages of Having Lipedema Surgery in Turkey
Advantages of Having Lipedema Surgery in TurkeyTurkey has become a global hub for lipedema surgery due to its skilled surgeons, modern facilities, and affordable healthcare options. In this post, we’ll explore the advantages of having lipedema surgery in ...
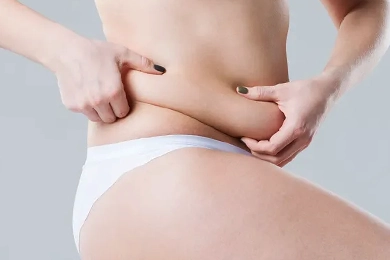 Why You Should Get a Tummy Tuck in Turkey
Why You Should Get a Tummy Tuck in TurkeyWhen considering a tummy tuck (abdominoplasty),selecting the right country for the procedure is crucial. Turkey has emerged as one of the top destinations for medical tourism, especially in the field of cosm ...
 What Causes Teeth Grinding?
What Causes Teeth Grinding?Teeth grinding, also known as bruxism, is a common issue that can affect both children and adults. This involuntary habit usually occurs during sleep but can also happen during the day. If left untreated, te ...
 Is There an Age Limit for Facial Stem Cell Therapy?
Is There an Age Limit for Facial Stem Cell Therapy?Facial stem cell therapy has become a popular option for those looking to rejuvenate their skin and combat signs of aging. This innovative procedure involves using a patient’s own stem cells to stimulate col ...
 Does Stem Cell Facial Rejuvenation Cause Cancer?
Does Stem Cell Facial Rejuvenation Cause Cancer?Stem cell facial rejuvenation has emerged as a cutting-edge anti-aging treatment in recent years. This procedure uses stem cells extracted from the patient's own body, which are then processed and injected i ...
 How Long Do the Effects of Facial Stem Cell Therapy Last?
How Long Do the Effects of Facial Stem Cell Therapy Last?Facial stem cell therapy has gained significant popularity in recent years as a powerful anti-aging treatment. By using stem cells from the patient's own body, this procedure helps rejuvenate and refresh the ...
 Are HIFU Results Permanent?
Are HIFU Results Permanent?High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound, commonly known as HIFU, has gained popularity as a non-surgical treatment for skin tightening and lifting. But one of the most frequently asked questions is: Are the result ...
 How Long Do the Effects of Non-Surgical Face Lifting (HIFU) Last?
How Long Do the Effects of Non-Surgical Face Lifting (HIFU) Last?Non-surgical face lifting methods, especially HIFU (High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound),have become a popular choice for skin tightening and rejuvenation. But one of the most common questions is: how long do ...
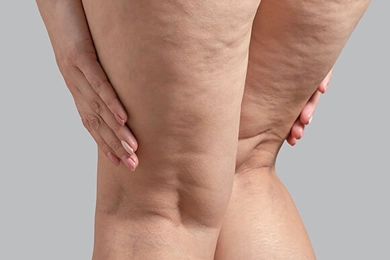 How to Know If You Have Lipedema: A Complete Guide
How to Know If You Have Lipedema: A Complete GuideA persistent medical condition called lipedema is sometimes confused with lymphedema or simply obesity. It is mainly affecting women and is characterized by an abnormal build-up of fat, usually in the arms a ...
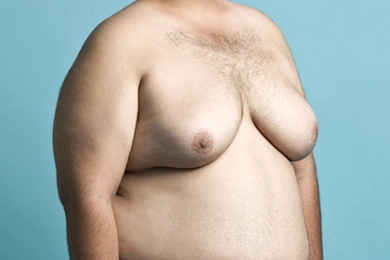 How to Know If You Have Gynecomastia?
How to Know If You Have Gynecomastia?If you suspect you have gynecomastia, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. Your doctor will perform a physical exam, evaluate your medical history, and may order blood tests to assess hormone ...