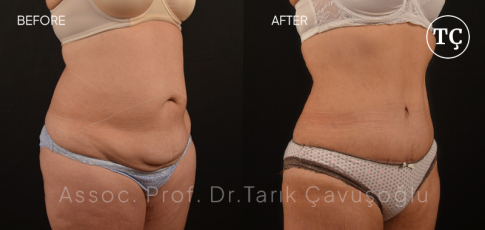
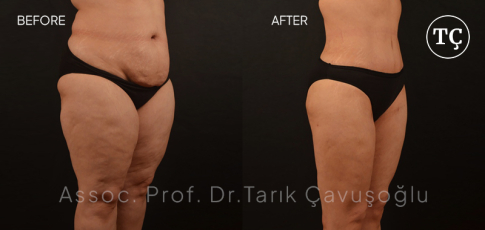
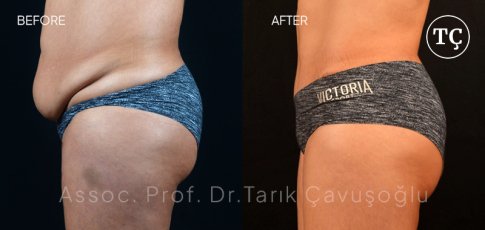
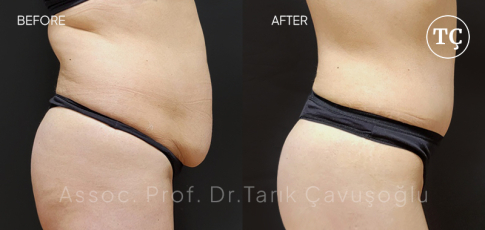
Vaser Liposuction
Vaser LiposuctionFirst-generation Vaser Liposuction devices, which were first used in the early 1990s, have completed their historical development process.
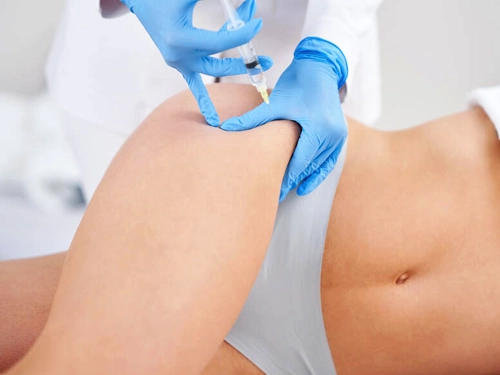 Laser Lipolysis
Laser LipolysisLaser lipolysis is the procedure of breaking down fat cells with the help of laser energy. While fat cells are broken down, capillaries in the surrounding tissue are also coagulated.
 Focused Ultrasound (hifu)
Focused Ultrasound (hifu)If you are fed up with the tired-looking face, if your wardrobe is full of creams called "miracle creams" and if you have tried all kinds of methods to create tightness on your face, but you could not achieve a desirable result, Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) might be the suitable option for you.
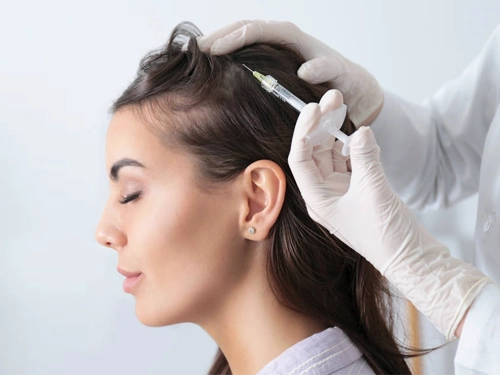 Hair Stem Cell Turkey
Hair Stem Cell TurkeyHair stem cell therapy is undoubtedly the most promising and advanced non-surgical treatment method for hair loss treatment until today. Stem cells are precursor cells found in the body that can develop into various cell types.
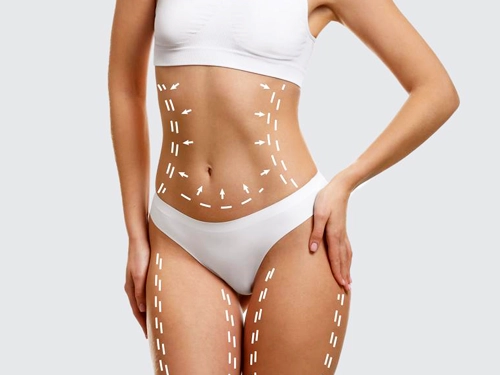 Mommy Makeover
Mommy MakeoverIf you need a mommy makeover, your doctor will plan an individual treatment for you according to your needs.
 Gynecomastia Surgery
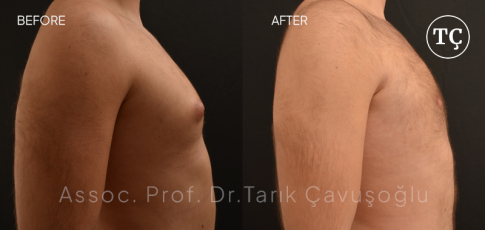
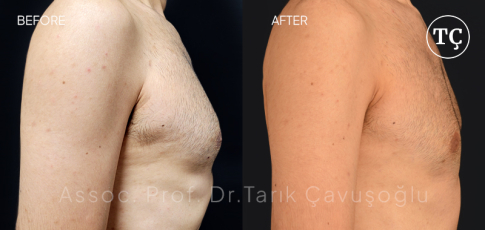
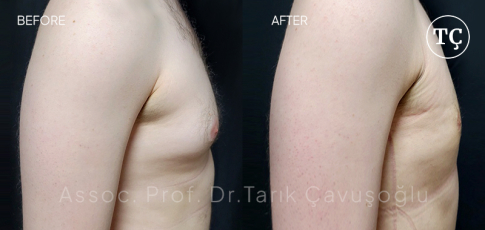
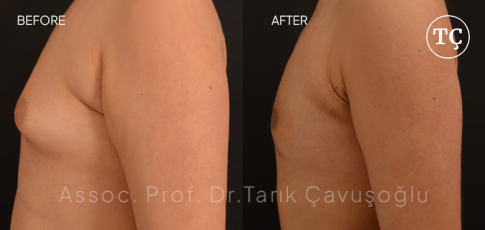
Gynecomastia SurgeryGynecomastia surgery, also referred to as male breast reduction, is an operation intended to treat the condition of gynecomastia, which is characterized by the growth of extra breast tissue in men.
 Tummy Tuck Surgery
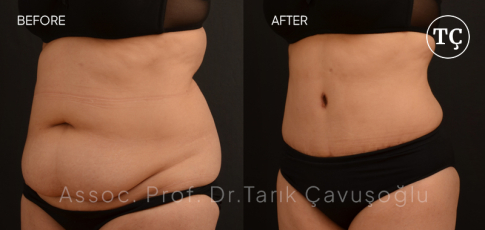
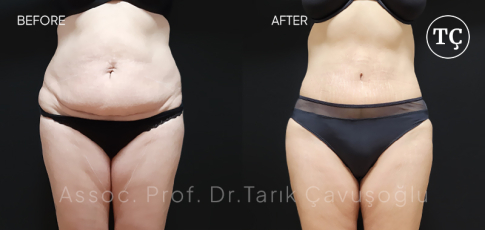
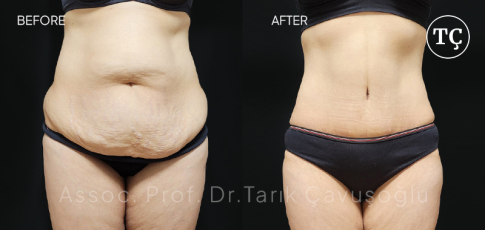
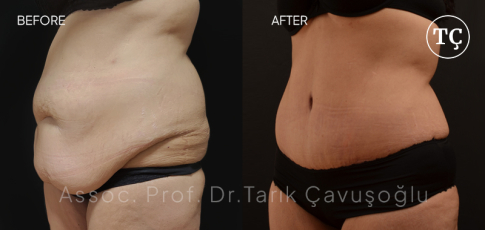
Tummy Tuck SurgeryAbdominoplasty or tummy tuck surgery is not only performed to tighten the deformed abdominal skin. By Tummy tuck surgery, it is also possible to repair muscular deformation that is caused by childbirth or weight changes.
 Hair Transplant Turkey Cost 2026
Hair Transplant Turkey Cost 2026Hair transplant is desired to achieve a natural and original appearance in hair transplant. It is not just about transplanting hair follicles into the balding areas.